|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
|
Modules | |
| printf Functionality for Buffer Module | |
Data Structures | |
| struct | buffer_t |
Macros | |
| #define | BUFFER_ALLOCATE(buffer_name,max_size) |
| #define | BUFFER_INIT(buffer_name, max_size) Buffer_Init(&buffer_name, &CAT2(buffer_name, _array)[0], max_size) |
| #define | BUFFER_ENQUEUE_FAILED 1 |
| enqueue failed (return value of Buffer_EnqueueData() ) More... | |
| #define | BUFFER_ENQUEUE_SUCCEEDED 0 |
| enqueue succeeded (return value of Buffer_EnqueueData() ) More... | |
Functions | |
| void | Buffer_Enqueue (buffer_t *buffer, uint8_t data) |
| uint8_t | Buffer_Dequeue (buffer_t *buffer) |
| uint16_t | Buffer_GetSize (buffer_t *buffer) |
| void | Buffer_Init (buffer_t *buffer, uint8_t *data_array, uint16_t max_size) |
| void | Buffer_SetCallback (buffer_t *buffer, void(*Callback)(buffer_t *buffer)) |
| void | Buffer_ClearCallback (buffer_t *buffer) |
| uint8_t | Buffer_EnqueueData (buffer_t *buffer, uint8_t *data, uint16_t length) |
This module implements a software FIFO buffer of bytes. It provides methods Buffer_Enqueue() and Buffer_Dequeue() to add and remove bytes from the buffer.
The user is responsible for allocating the structure used to manage the buffer, buffer_t, as well as the actual byte array which will be used to implement the buffer. These are then passed to Buffer_Init() which must be called prior to any attempts to Enqueue or Dequeue.
There is also a Buffer_EnqueueData() method which allows multiple bytes to be added to the buffer at once.
An alternative to this FIFO byte buffer is the Item Buffer module which works the same except with items of any size instead of being limited to bytes only.
| #define BUFFER_ALLOCATE | ( | buffer_name, | |
| max_size | |||
| ) |
Helpful macros for allocating and initializing buffer module
BUFFER_ALLOCATE uses a name to declare the array and buffer structure
BUFFER_INIT uses the name given in BUFFER_ALLOCATE to initialize the buffer structure
| #define BUFFER_ENQUEUE_FAILED 1 |
enqueue failed (return value of Buffer_EnqueueData() )
| #define BUFFER_ENQUEUE_SUCCEEDED 0 |
enqueue succeeded (return value of Buffer_EnqueueData() )
| #define BUFFER_INIT | ( | buffer_name, | |
| max_size | |||
| ) | Buffer_Init(&buffer_name, &CAT2(buffer_name, _array)[0], max_size) |
| void Buffer_ClearCallback | ( | buffer_t * | buffer | ) |
Clear/remove the callback function for 'buffer'
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure whose callback function is to be cleared |
| uint8_t Buffer_Dequeue | ( | buffer_t * | buffer | ) |
Buffer_Dequeue will return one item from the front of the FIFO buffer
Buffer_Dequeue will return the item at the front of the FIFO buffer then increment (and wrap as needed) the front. If the buffer is empty it will return 0.
Buffer_Init() must be used to initialize the buffer prior to calling Buffer_Dequeue and passing it a pointer to the buffer.
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure holding the buffer info |
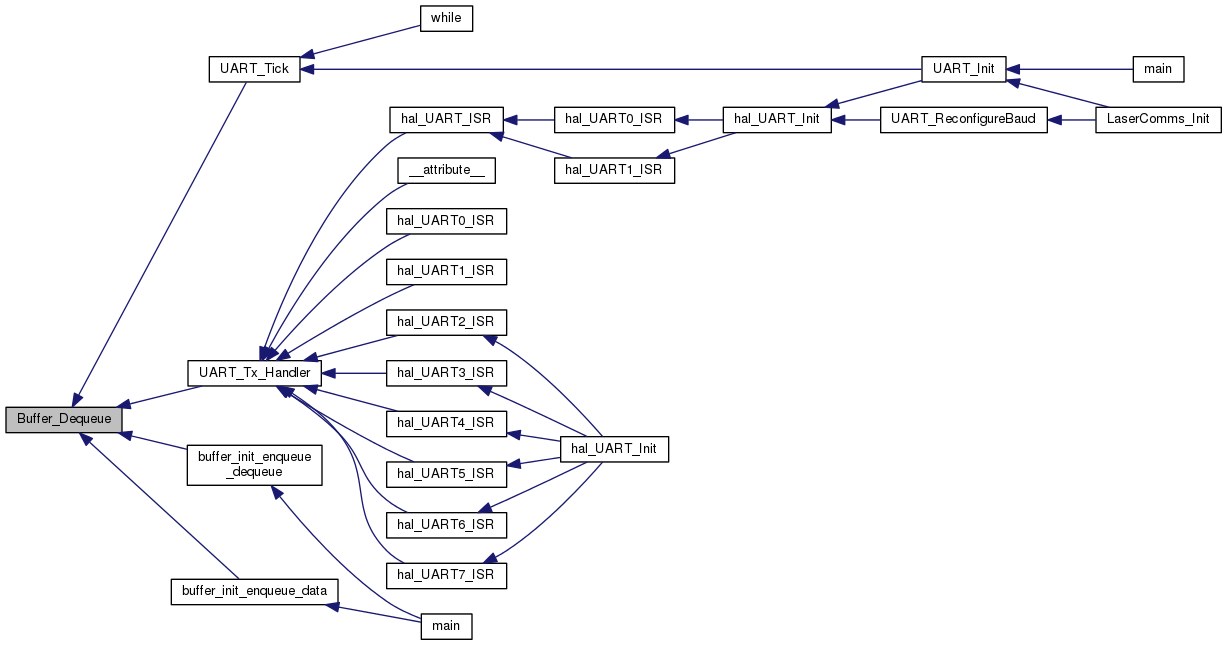
| void Buffer_Enqueue | ( | buffer_t * | buffer, |
| uint8_t | data | ||
| ) |
Buffer_Enqueue will add one item, data, to the FIFO buffer
Buffer_Enqueue will add one item to the rear of the data buffer then increment (and wrap is needed) the rear. If the buffer is full it will overwrite the data at the front of the buffer and increment the front.
Buffer_Init() must be used to initialize the buffer prior to calling Buffer_Enqueue and passing it a pointer to the buffer.
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure holding the buffer info |
| data | char data to be added to the rear of the FIFO buffer |
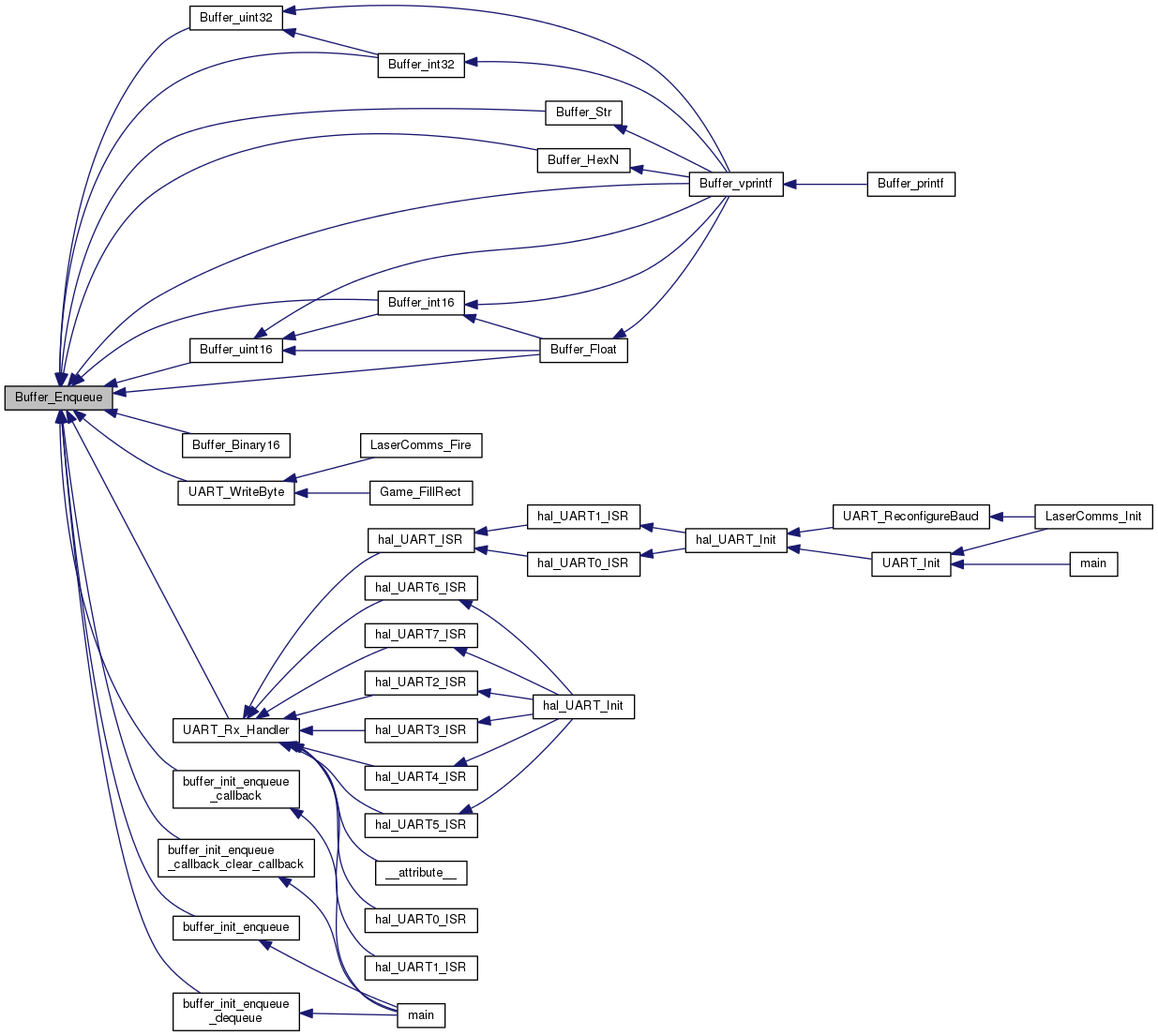
| uint8_t Buffer_EnqueueData | ( | buffer_t * | buffer, |
| uint8_t * | data, | ||
| uint16_t | length | ||
| ) |
Queue a array of data to the buffer
Buffer_EnqueueData will add an array of items to the rear of the data buffer and increment (and wrap if needed) the rear. If the buffer does not have room none of the data will be queued to the buffer.
Buffer_Init() must be used to initialize the buffer prior to calling Buffer_EnqueueData and passing it a pointer to the buffer.
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure holding the buffer info |
| data | byte pointer to data array to be added to the rear of the FIFO buffer |
| length | the number of items in the data array |
| uint16_t Buffer_GetSize | ( | buffer_t * | buffer | ) |
Buffer_GetSize returns the number of items in the FIFO buffer
Buffer_Init() should be used to initialize the buffer otherwise the return value will be meaningless
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure holding the buffer info |
| void Buffer_Init | ( | buffer_t * | buffer, |
| uint8_t * | data_array, | ||
| uint16_t | max_size | ||
| ) |
Initialize a FIFO buffer
Example code:
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure to be initialized |
| data_array | Array of char data to implement the actual buffer |
| max_size | Maximum size of the buffer (should be the same length as the array) |
Set Callback function for buffer to be called after items are Queued to the buffer
The callback function will be called after anything is Queued to the buffer. The function will be called with a pointer to the buffer which had a byte queued onto it.
Example:
This example is useful for a uC which has a hardware Tx interrupt flag which is set whenever there is room in the hardware Tx FIFO buffer. When done transmitting the interrupt must be disabled to avoid getting stuck in the ISR. When data needs to be sent the interrupt must be enabled again, thus the need for the callback.
Another usage could be to handle received data on a receive buffer.
| buffer | Pointer to the buffer_t data structure whose callback function is to be set |
| Callback | Function pointer to a callback function with no return value and a buffer_t pointer input. |