|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
|
Functions | |
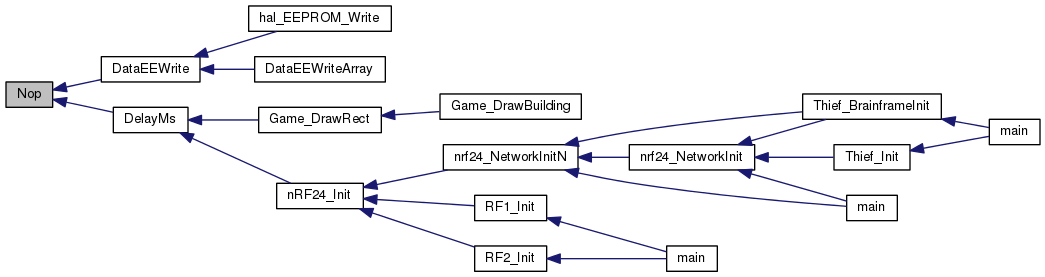
| void | Nop (void) |
| No oporation. More... | |
| void | DisableInterrupts (void) |
| Disable global interrupts. More... | |
| void | EnableInterrupts (void) |
| Configure and enable global interrupts. More... | |
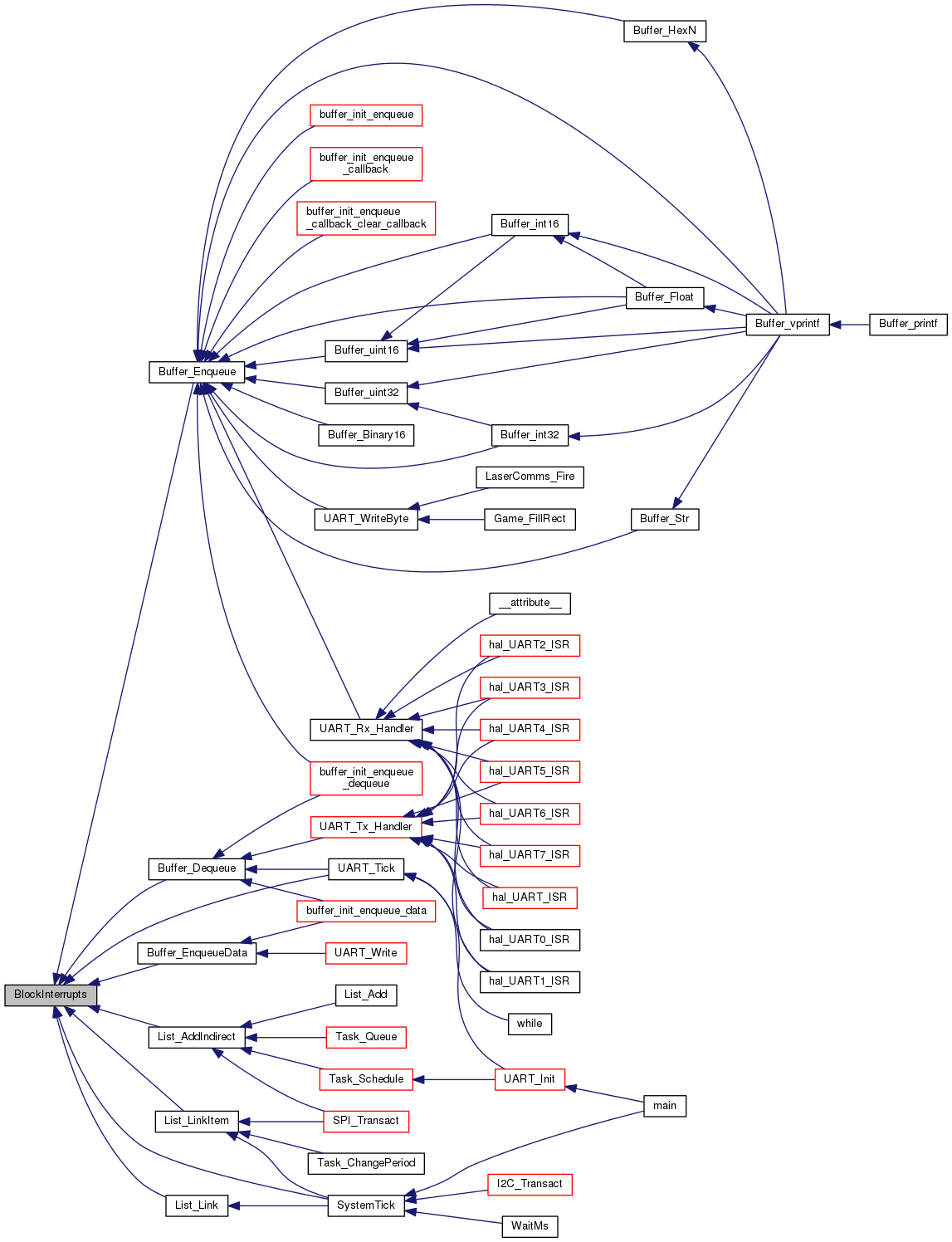
| void | BlockInterrupts (void) |
| Backup the interrupt status (i.e. IPL) and block interrupts. More... | |
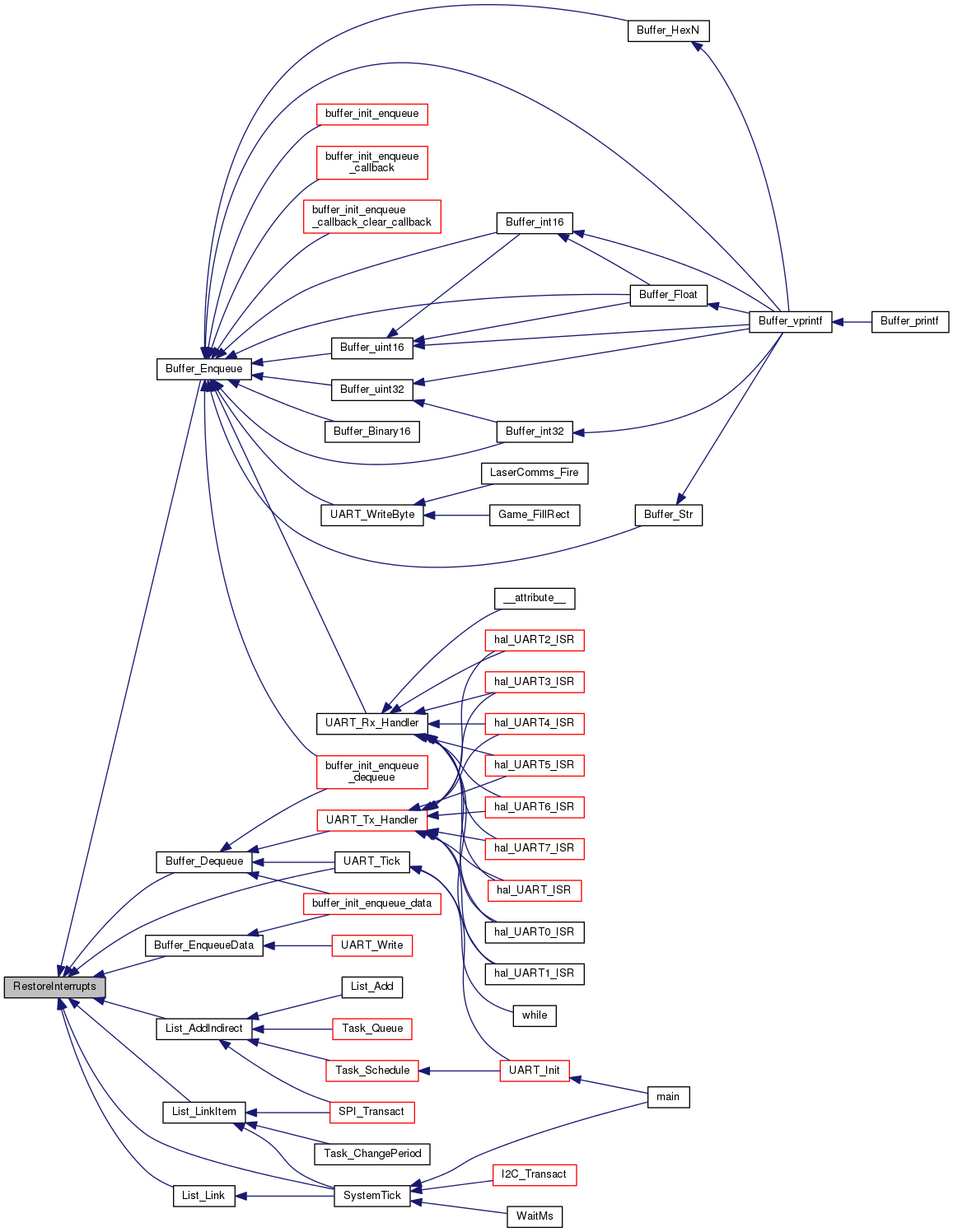
| void | RestoreInterrupts (void) |
| RestoreInterrupts after blocking interrupts (BlockInterrupts()) More... | |
The hal_general.h file is processor specific and should be located in each processors directory within hal / processor family.
Each of the following function prototypes are typically implemented with macros are not actual functions.
| void BlockInterrupts | ( | void | ) |
Backup the interrupt status (i.e. IPL) and block interrupts.
A interrupt safe method to block interrupts and restore to the appropriate state using the matching RestoreInterrupts function.
| void DisableInterrupts | ( | void | ) |
Disable global interrupts.
Disable global interrupts. This can destroy the interrupt status of the CPU and should never be called from an interrupt.

| void EnableInterrupts | ( | void | ) |
Configure and enable global interrupts.
Configures multi vectored interrupts where available. Will not restore the interrupt level. See BlockInterrupts() and RestoreInterrupts()

| void Nop | ( | void | ) |
No oporation.
Note: this may already be implemented for some microcontrollers (i.e. PIC).
| void RestoreInterrupts | ( | void | ) |
RestoreInterrupts after blocking interrupts (BlockInterrupts())
Restores the interrupt status that was backed up by BlockInterrupts() and enables interrupts.