|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
|
embedded-software
reusable software modules for embedded systems
|
The Task Management Module implements a task queue and a task schedule. More...
Macros | |
| #define | TASK_MAX_LENGTH 20 |
| #define | TASK_ROLL_TIME (TIME_MAX-(uint32_t)10*24*60*60*1000) |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void(* | task_fn_pointer_input_t )(void *) |
| typedef void(* | task_t )(void) |
Functions | |
| void | Task_Init (void) |
| void | SystemTick (void) |
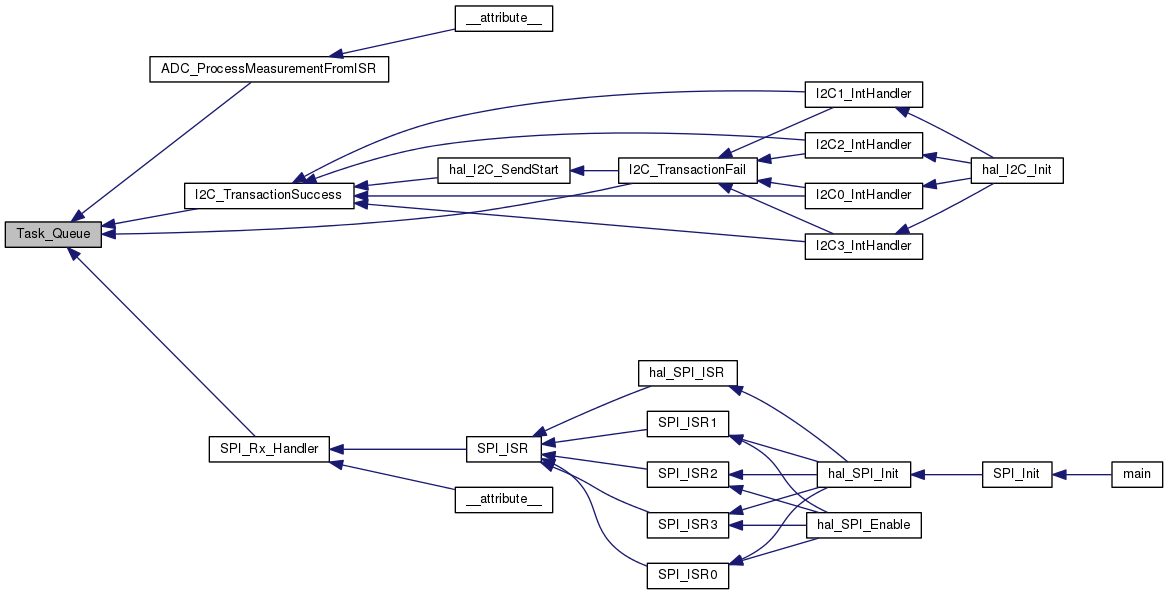
| void | Task_Queue (task_t fn, void *pointer) |
| Adds a function to the task queue. More... | |
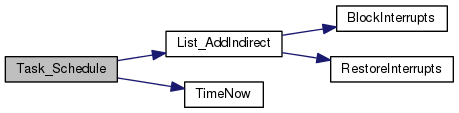
| int8_t | Task_Schedule (task_t fn, void *pointer, uint32_t delay, uint32_t period) |
| Adds task to be scheduled for execution. More... | |
| int8_t | Task_SetIdleTask (task_t fn) |
| Sets a task to run whenever the task queue is empty / no tasks due to run. More... | |
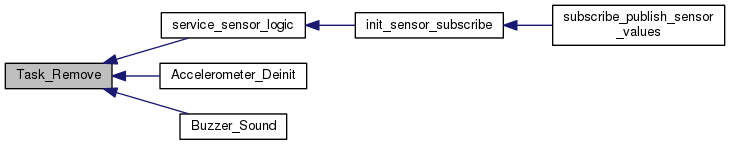
| void | Task_Remove (task_t fn, void *pointer) |
| Removes Task. More... | |
| void | WaitMs (uint32_t wait) |
| uint8_t | Task_IsScheduled (task_t fn) |
| void | Task_ChangePeriod (task_t fn, uint32_t period, uint8_t update_next_time) |
The Task Management Module implements a task queue and a task schedule.
The task queue is a single linked FIFO list. Each time SystemTick() is called the first task in the queue will execute. If the task is periodic it will be added back to the task schedule once it is ran.
The task schedule is a single linked list of tasks in order of when they are scheduled to run. If two tasks are scheduled for the same time there is no guarantee which task will run first. Each task scheduled has a timestamp which indicates when it ran last and the period if it is to be run again. If the task was just added to the schedule then time ran will indicate the time it should first nun minus the period. When SystemTick() is called it will check if any scheduled tasks are due to run and add them to the task queue when they are due.
UPDATED 10/4/2012 Remove functions were not interrupt safe -> Fixed
UPDATED 2/18/2014 Fixed bug in linking multiple tasks at once and/or scheduling multiple tasks at once. Added extra checks to ensure task index is in range everytime the task array is accessed.
UPDATED 3/1/2016 Task_Remove for the task that is running was not working because the task was not linked in the list. Task_Remove was update to traverse the entire array of tasks instead of using List_GetItem.
| #define TASK_MAX_LENGTH 20 |
The number of tasks that can be added to the task queue or task schedule or task trigger list
Note: the task queue and task schedule list use the same array of tasks in implementing the linked lists. If the array becomes full the module will drop the task that is to be added.
| #define TASK_ROLL_TIME (TIME_MAX-(uint32_t)10*24*60*60*1000) |
The time when the task management system will force the timer to roll over
The task management module schedules tasks in the future by setting the time to run as some time in the future. Once the current time + the period exceeds TIME_MAX the task time to run will roll over and cause the task to run erroneously. Thus the task managemnent system must force the timing module's internal time to rollover prior to when it would natrually roll over (TIME_MAX). The default is 10 days prior to TIME_MAX which means the task managment system can only handle tasks scheduled within 10 days and no longer.
| typedef void(* task_fn_pointer_input_t)(void *) |
helpful typedef's for casting functions if you want to avoid the incompatible pointers warning
| typedef void(* task_t)(void) |
default task type
| void SystemTick | ( | void | ) |
Run the first task in the task queue and check if any tasks are due to run in the schedule
Run the first task in the task queue provided one exists. If the task ran has a period value then it will be moved to the task schedule instead of removed.
Check if any of the scheduled tasks are due to run. If so move any tasks whose run time is at or before the current time to the task queue where they will be ordered by priority and executed accordingly.
If the Event Module is included check for events
| void Task_ChangePeriod | ( | task_t | fn, |
| uint32_t | period, | ||
| uint8_t | update_next_time | ||
| ) |
Update the period of an existing task
| fn | pointer to the function whose task should be updated |
| period | new period |
| update_next_time | 0 - don't rescheule the next run, 1 reschedule the next run base on the new period |
| void Task_Init | ( | void | ) |
Initialize Task Management Module
Initializes the task management module for operation.
| uint8_t Task_IsScheduled | ( | task_t | fn | ) |
Checks if a task is scheduled or queued
| fn | function to look for |
| void Task_Queue | ( | task_t | fn, |
| void * | pointer | ||
| ) |
Adds a function to the task queue.
Task_Queue() adds a task to be run by the task management system to the queue. Use this function to add the function to be run
| fn | Function Pointer - must have no return value, can have a pointer input or no input. If it has an input then you may want to cast it using (task_fn_pointer_input_t) to avoid compiler warning about |
| pointer | pointer to pass to the task when run. Set to 0 if the task has no input |
| void Task_Remove | ( | task_t | fn, |
| void * | pointer | ||
| ) |
Removes Task.
RemoveTask() loops through the entire task management queue and schedule and removes that task from the task management system.
If the task could be in the list more than once they will all be removed if pointer is 0. If their are multiple tasks with the same pointer then you should call Task_Remove as many times as you suspect the task may be in the list.
| fn | Function Pointer - must have no return value, can have a pointer input or no input. If it has an input then you may want to cast it using (task_fn_pointer_input_t) to avoid compiler warning about |
| pointer | Input Pointer, if the function has no input pointer or if you want to remove all fn functions regardless of the pointer then make pointer 0 |

| int8_t Task_Schedule | ( | task_t | fn, |
| void * | pointer, | ||
| uint32_t | delay, | ||
| uint32_t | period | ||
| ) |
Adds task to be scheduled for execution.
This function adds a task that is scheduled for later time. Tasks are order strictly by their time (FIFO)
Note: tasks are not guaranteed to run at the exact time specified by delay and period. Timing will depend on how often SystemTick(). In properly designed systems SystemTick() should be called frequently enough to keep the number of tasks in the queue low so scheduled tasks are run on time.
| fn | Function Pointer - must have no return value, can have a pointer input or no input. If it has an input then you may want to cast it using (task_fn_pointer_input_t) to avoid compiler warning about |
| pointer | pointer to pass to the task when run. Set to 0 if the task has no input |
| delay | Delay before the task is first run |
| period | Period of how often the task is run (0 no rescheduling) |
| int8_t Task_SetIdleTask | ( | task_t | fn | ) |
Sets a task to run whenever the task queue is empty / no tasks due to run.
| fn | Function Pointer - must have no return value and no input. |
| void WaitMs | ( | uint32_t | wait | ) |
Wait a set number of milliseconds and run queued or scheduled tasks while waiting
WaitMs is similar to DelayMs from Timer Module, exception being that it repeatedly calls SystemTick() to allow functions to be run from the Queue and the Schedule.
| wait | time amount for the wait |